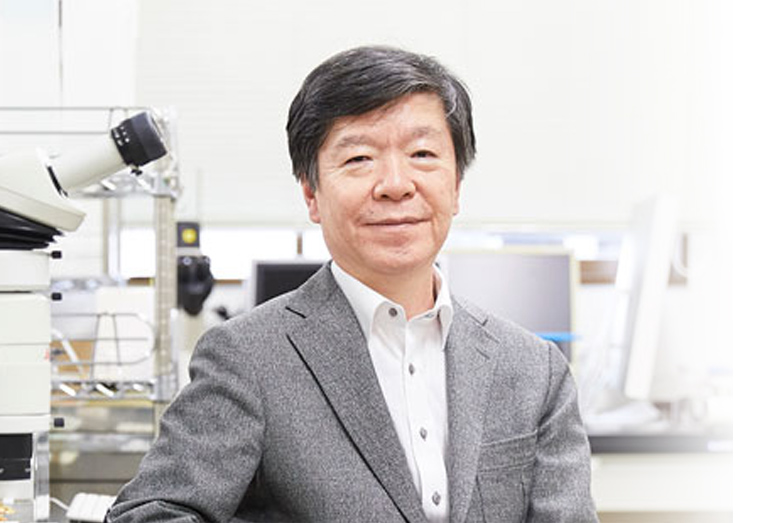
チームリーダー
西田 栄介
Ph.D.
老化分子生物学研究チーム
[2025年3月 終了]
E-mail eisuke.nishida[at]riken.jp
[at]を@に変えてください
地球上の多種多様な生物にはそれぞれ固有の寿命があります。さらに、同一生物種においても寿命には個体によりバラつきがあります。そのような種間並びに個体間に差の大きい寿命あるいは老化速度が、種を超えた共通のメカニズムによって制御されていることが分かってきています。その共通の老化・寿命制御メカニズムの発見は、ごく小さい(1ミリ程度)モデル生物である線虫を用いた研究が契機となって明らかになってきました。老化・寿命は、『生まれ(遺伝的要因)』と『育ち(環境要因)』によって大きく影響を受けることが分かってきています。私たちの研究室では、主に線虫と小型魚類を材料として用い、老化・寿命制御の分子メカニズムの解析をしています。
研究テーマ
- 組織間コミュニケーションによる老化速度制御の解明
- エピゲノム修飾による老化速度制御の解明
- エピゲノム変化の次世代への継承機構の解明
主要論文
Okabe E, Uno M, Kishimoto S, Nishida E.
Intertissue small RNA communication mediates the acquisition and inheritance of hormesis in Caenorhabditis elegans.
Communications biology
4, 207 (2021)
doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-01692-3
Takahashi TM, Sunagawa GA, Soya S, et al.
A discrete neuronal circuit induces a hibernation-like state in rodents.
Nature
583, 109-114 (2020)
doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2163-6
Nono M, Kishimoto S, Sato-Carlton A, et al.
Intestine-to-Germline Transmission of Epigenetic Information Intergenerationally Ensures Systemic Stress Resistance in C. elegans..
Cell Reports
30, 3207-3217 (2020)
doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.02.050
Ikeda T, Uno M, Honjoh S, Nishida E.
The MYST family histone acetyltransferase complex regulates stress resistance and longevity through transcriptional control of DAF-16/FOXO transcription factors.
EMBO Reports
18(10), 1716-1726 (2017)
doi: 10.15252/embr.201743907
Kishimoto S, Uno M, Okabe E, et al.
Environmental stresses induce transgenerationally inheritable survival advantages via germline-to-soma communication in Caenorhabditis elegans.
Nature Communications
8, 14031. (2017)
doi: 10.1038/ncomms14031
Miyatake K, Kusakabe M, Takahashi C, Nishida E.
ERK7 regulates ciliogenesis by phosphorylating the actin regulator CapZIP in cooperation with Dishevelled.
Nature Communications
6, 6666 (2015)
doi: 10.1038/ncomms7666
Takahashi C, Kusakabe M, Suzuki T, et al.
mab21-l3 regulates cell fate specification of multiciliate cells and ionocytes.
Nature Communications
6, 6017 (2015)
doi: 10.1038/ncomms7017
Imajo M, Ebisuya M, Nishida E.
Dual role of YAP and TAZ in renewal of the intestinal epithelium.
Nature Cell Biology
17(1), 7-19 (2015)
doi: 10.1038/ncb3084
Sunadome K, Suzuki T, Usui M, et al.
Antagonism between the Master Regulators of Differentiation Ensures the Discreteness and Robustness of Cell Fates.
Molecular Cell
54(3), 526-535 (2014)
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.03.005
Uno M, Honjoh S, Matsuda M, et al.
A fasting-responsive signaling pathway that extends life span in C. elegans.
Cell Reports
3(1), 79-91 (2013)
doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.12.018
Okuyama T, Inoue H, Ookuma S, et al.
The ERK-MAPK pathway regulates longevity through SKN-1 and insulin-like signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans.
Journal of Biological Chemistry
285(39), 30274-30281 (2010)
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.146274
Hanafusa H, Matsumoto K, Nishida E.
Regulation of ERK activity duration by Sprouty contributes to dorsoventral patterning.
Nature Cell Biology
11, 106-109 (2009)
doi: 10.1038/ncb1820
Honjoh S, Yamamoto T, Uno M, Nishida E.
Signaling through RHEB-1 mediates intermittent fasting-induced longevity in C. elegans.
Nature
457, 726-730 (2009)
doi: 10.1038/nature07583
メンバー
宇野 雅晴
上級研究員
髙橋 知佳
研究員
岡部 恵美子
研究員
ニュース

2025年3月28日 研究成果
iPS心組織で電気信号の流れを改善
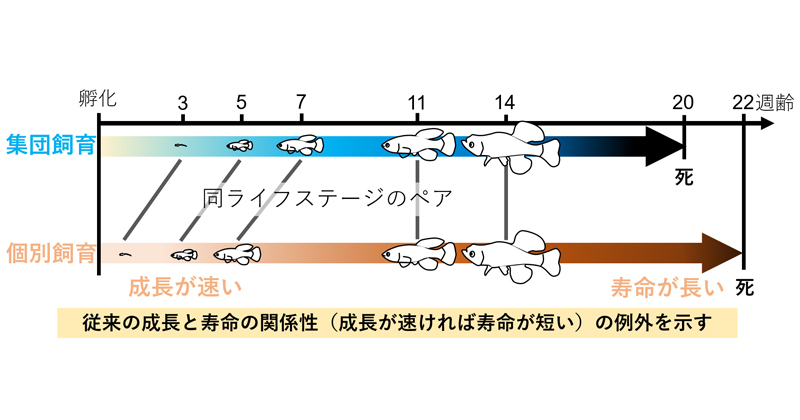
2024年9月30日 研究成果
早熟でも早老・短命にならない例外の生活史特性を発見

2024年6月26日 BDRニュース
研究者にズームイン
老化の本質に迫る ヒトは若返ることができるのか?
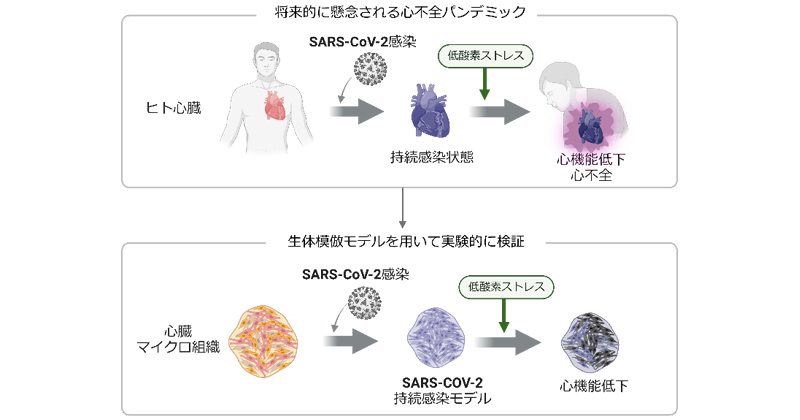
2023年12月23日 研究成果
「ポストコロナ」で警戒すべき心不全パンデミック

2023年10月11日 BDRニュース
BDRの研究ネホリハホリ
新しい寿命研究のモデル生物
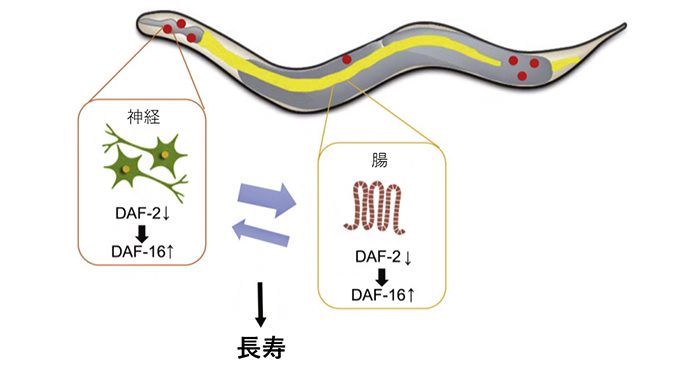
2021年7月5日 研究成果
寿命を制御する組織間相互作用
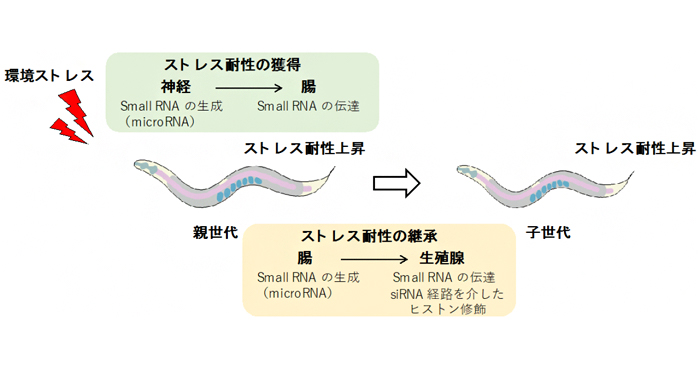
2021年2月17日 研究成果
ホルミシス効果の獲得と継承を担う小分子RNA

2020年12月7日 BDRニュース
FACE: ヒトの冬眠に挑む研究者
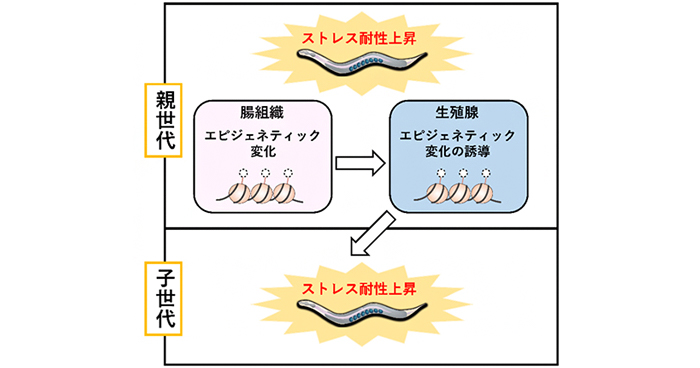
2020年3月11日 研究成果
ストレス耐性は親から子へ継承される

2019年7月31日 BDRニュース
BDRの研究ネホリハホリ
老化の研究は、コツコツ

2019年7月19日 BDRニュース
西田栄介センター長が第60回藤原賞を受賞