Team Leader
Eisuke Nishida
Ph.D.
Laboratory for Molecular Biology of Aging
[Closed Mar. 2025]
LocationKobe / Developmental Biology Buildings
E-maileisuke.nishida@riken.jp
The organismal lifespan varies from species to species, and it also varies among individuals of the same species. Despite such large differences in the organismal lifespan or the rate of aging, recent studies suggest the existence of the common mechanisms of lifespan/aging regulation. The best studied common mechanism of lifespan regulation came from the research using a tiny soil worm called C. elegans. Both “nature (genetic factors)” and “nurture (environmental factors)” are shown to influence lifespan/aging. Our laboratory uses C. elegans and small fish to understand the molecular mechanisms underlying lifespan regulation by genetic and environmental factors.
Research Theme
- Inter-organ communications underlying aging regulation
- Epigenomic regulation of aging
- Mechanisms of transgenerational inheritance of epigenetic memories
Selected Publications
Okabe E, Uno M, Kishimoto S, Nishida E.
Intertissue small RNA communication mediates the acquisition and inheritance of hormesis in Caenorhabditis elegans.
Communications biology
4, 207 (2021)
doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-01692-3
Takahashi TM, Sunagawa GA, Soya S, et al.
A discrete neuronal circuit induces a hibernation-like state in rodents.
Nature
583, 109-114 (2020)
doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2163-6
Nono M, Kishimoto S, Sato-Carlton A, et al.
Intestine-to-Germline Transmission of Epigenetic Information Intergenerationally Ensures Systemic Stress Resistance in C. elegans..
Cell Reports
30, 3207-3217 (2020)
doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.02.050
Ikeda T, Uno M, Honjoh S, Nishida E.
The MYST family histone acetyltransferase complex regulates stress resistance and longevity through transcriptional control of DAF-16/FOXO transcription factors.
EMBO Reports
18(10), 1716-1726 (2017)
doi: 10.15252/embr.201743907
Kishimoto S, Uno M, Okabe E, et al.
Environmental stresses induce transgenerationally inheritable survival advantages via germline-to-soma communication in Caenorhabditis elegans.
Nature Communications
8, 14031. (2017)
doi: 10.1038/ncomms14031
Miyatake K, Kusakabe M, Takahashi C, Nishida E.
ERK7 regulates ciliogenesis by phosphorylating the actin regulator CapZIP in cooperation with Dishevelled.
Nature Communications
6, 6666 (2015)
doi: 10.1038/ncomms7666
Takahashi C, Kusakabe M, Suzuki T, et al.
mab21-l3 regulates cell fate specification of multiciliate cells and ionocytes.
Nature Communications
6, 6017 (2015)
doi: 10.1038/ncomms7017
Imajo M, Ebisuya M, Nishida E.
Dual role of YAP and TAZ in renewal of the intestinal epithelium.
Nature Cell Biology
17(1), 7-19 (2015)
doi: 10.1038/ncb3084
Sunadome K, Suzuki T, Usui M, et al.
Antagonism between the Master Regulators of Differentiation Ensures the Discreteness and Robustness of Cell Fates.
Molecular Cell
54(3), 526-535 (2014)
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.03.005
Uno M, Honjoh S, Matsuda M, et al.
A fasting-responsive signaling pathway that extends life span in C. elegans.
Cell Reports
3(1), 79-91 (2013)
doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.12.018
Okuyama T, Inoue H, Ookuma S, et al.
The ERK-MAPK pathway regulates longevity through SKN-1 and insulin-like signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans.
Journal of Biological Chemistry
285(39), 30274-30281 (2010)
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.146274
Hanafusa H, Matsumoto K, Nishida E.
Regulation of ERK activity duration by Sprouty contributes to dorsoventral patterning.
Nature Cell Biology
11, 106-109 (2009)
doi: 10.1038/ncb1820
Honjoh S, Yamamoto T, Uno M, Nishida E.
Signaling through RHEB-1 mediates intermittent fasting-induced longevity in C. elegans.
Nature
457, 726-730 (2009)
doi: 10.1038/nature07583
Members
Masaharu Uno
Senior Research Scientist
Chika Takahashi
Research Scientist
Emiko Okabe
Research Scientist
News

Oct. 11, 2023 BDR News
Dive into BDR's intriguing research
A new model organism for lifespan research
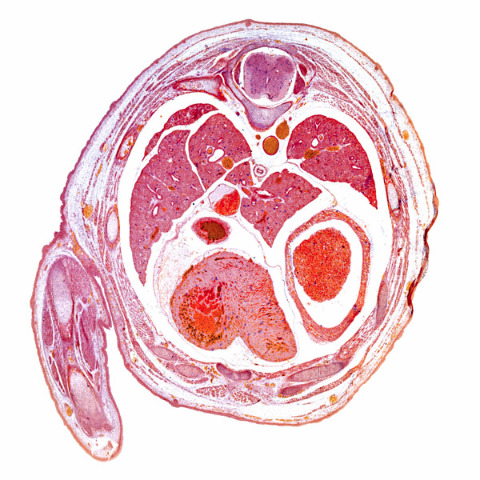
Apr. 14, 2023 Research
How mouse embryos determine left from right

Dec. 25, 2020 Research
Hijacking hibernation
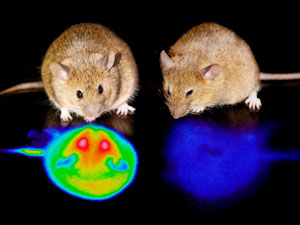
Aug. 28, 2020 Research
A neural circuit that makes rodents go into a hibernation-like state found

Jul. 31, 2019 BDR News
Dive into BDR's intriguing research
A Step-by-step Approach to Aging Research