チームリーダー
二階堂 愛
Ph.D.
バイオインフォマティクス研究開発チーム
[2025年4月より 最先端研究プラットフォーム連携(TRIP)事業本部 科学研究基盤モデル開発プログラム(AGIS)に所属が変わりました]
E-mail itoshi.nikaido@riken.jp
多細胞生物の生命活動の最小単位はひとつひとつの細胞です。我々のグループは、1 細胞から生命を理解する計測や摂動技術を開発します。DNA シーケンス技術の発展により高速に大量のDNA 配列が得られるようになりました。そこで、多細胞生物が示す複雑で様々な生命現象を1 細胞ごとに核酸へ変換し、超並列DNA シーケンスで読み取り、数理科学の力で生命情報を取り出します。
我々はこれまで高精度・高出力な1 細胞RNA シーケンスであるQuartz-Seq2 の開発や、世界初の1 細胞完全長Total RNA シーケンス法RamDA-seq の開発に成功してきました。我々のグループは、これらの技術をもとに、ゲノム編集技術、マイクロ流体デバイス、人工知能技術なども駆使しながら、細胞の命運や機能、エピゲノム変化などを捉える新しい1 細胞シーケンス技術の開発を目指します。
さらに、これらの方法を用いて、理研内外の様々なライフサイエンス分野の研究者と共同研究を進めます。
研究テーマ
- 新しい1細胞オミックス計測技術の開発
- 新しい1細胞オミックスを用いた連携
主要論文
Lin CW, Septyaningtrias DE, Chao HW, et al.
A common epigenetic mechanism across different cellular origins underlies systemic immune dysregulation in an idiopathic autism mouse model.
Molecular Psychiatry
27(8), 3343-3354 (2022)
doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01566-y
Ochiai H, Hayashi T, Umeda M, et al.
Genome-wide kinetic properties of transcriptional bursting in mouse embryonic stem cells.
Science Advances
6(25), eaaz6699 (2020)
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz6699
Ozaki H, Hayashi T, Umeda M, Nikaido I.
Millefy: visualizing cell-to-cell heterogeneity in read coverage of single-cell RNA sequencing datasets.
BMC Genomics
21, 177 (2020)
doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-6542-z
Tsuyuzaki K, Sato H, Sato K, Nikaido I.
Benchmarking principal component analysis for large-scale single-cell RNA-sequencing.
Genome Biology
21, 9 (2020)
doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1900-3
Mereu E, Lafzi A, Moutinho C, et al.
Benchmarking single-cell RNA-sequencing protocols for cell atlas projects.
Nature biotechnology
38(6), 747-755 (2020)
doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0469-4
Sato K, Tsuyuzaki K, Shimizu K, Nikaido I.
CellFishing.jl: an ultrafast and scalable cell search method for single-cell RNA-sequencing.
Genome Biology
20, 31 (2019)
doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1639-x
Sasagawa Y, Danno H, Takada H et al.
Quartz-Seq2: a high-throughput single-cell RNA-sequencing method that effectively uses limited sequence reads.
Genome Biology
19, 29 (2018)
doi: 10.1186/s13059-018-1407-3
Hayashi T, Ozaki H, Sasagawa Y, et al.
Single-cell full-length total RNA sequencing uncovers dynamics of recursive splicing and enhancer RNAs.
Nature Communications
9, 619 (2018)
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-02866-0
Matsumoto H, Kiryu H, Furusawa C, et al.
SCODE: An efficient regulatory network inference algorithm from single-cell RNA-Seq during differentiation.
Bioinformatics
33(15), 2314-2321 (2017)
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx194
Tsuyuzaki K, Morota G, Ishii M, et al.
MeSH ORA framework: R/Bioconductor packages to support MeSH over-representation analysis.
BMC Bioinformatics
16, 45 (2015)
doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0453-z
Sasagawa Y, Nikaido I, Hayashi T, et al.
Quartz-Seq: a highly reproducible and sensitive single-cell RNA sequencing method, reveals non-genetic gene-expression heterogeneity.
Genome Biology
14, 3097 (2013)
doi: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-4-r31
Adachi K, Nikaido I, Ohta H, et al.
Context-dependent wiring of Sox2 regulatory networks for self-renewal of embryonic and trophoblast stem cells.
Molecular Cell
52, 380-392 (2013)
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.09.002
ニュース

2023年7月10日 研究成果
芽を生み出すかどうか、植物カルス細胞の分化を運命づける因子をつきとめた 植物の器官再生能力を制御する新たな仕組みを発見

2023年6月30日 研究成果
最前線で胃を守れ

2022年5月1日 研究成果
自閉症原因は胎児の時から?

2021年7月12日 研究成果
遺伝子の構造が「密」になると遺伝子の働きが抑制される
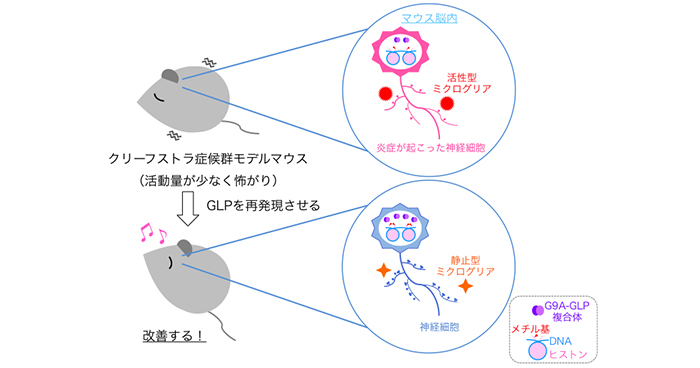
2021年7月6日 研究成果
エピゲノム異常に起因する脳機能不全の治療の可能性

2020年9月1日 BDRニュース
BDRの研究ネホリハホリ
最先端研究の「縁の下の力持ち」

2020年6月18日 研究成果
哺乳類細胞における突発的遺伝子発現動態を網羅的に決定!!
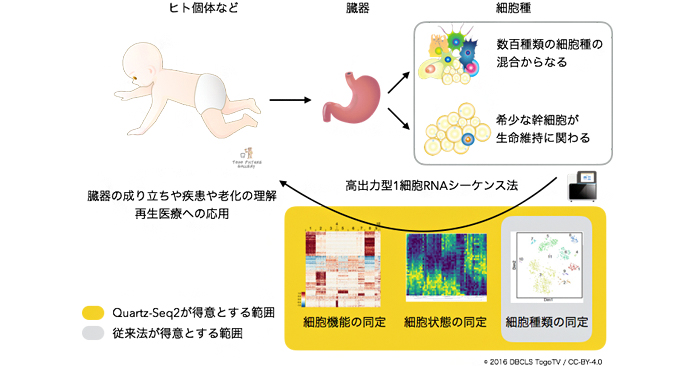
2020年4月7日 研究成果
1細胞RNA解析で世界最高成績

2020年3月3日 研究成果
見逃されていた細胞ごとのばらつきを可視化するソフトウェアを開発
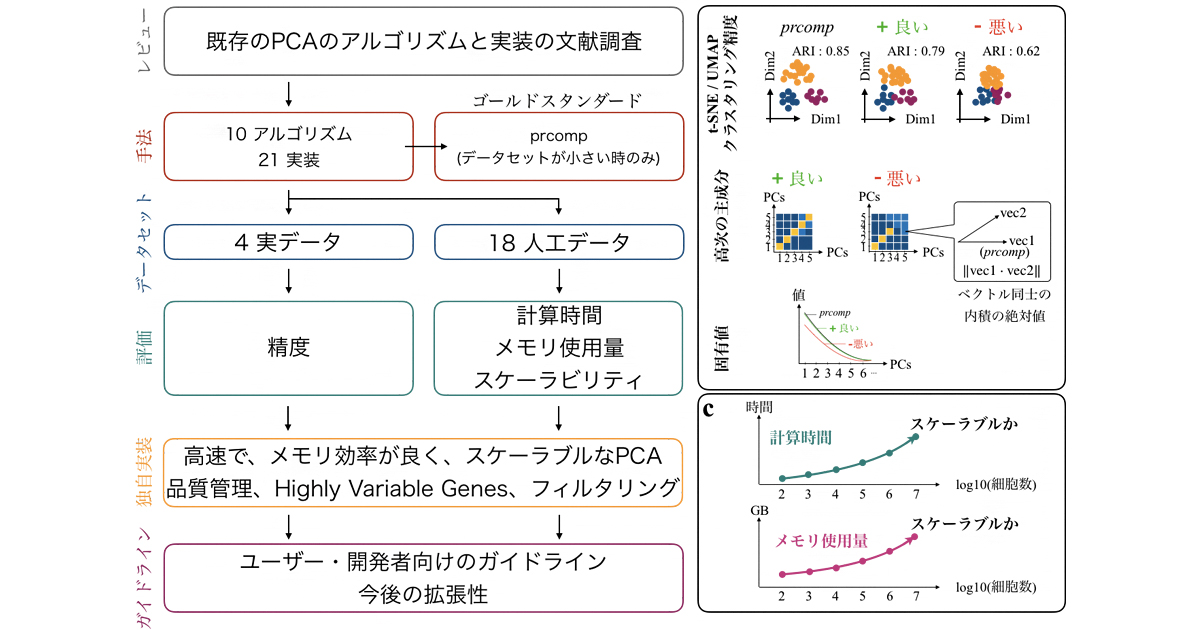
2020年1月20日 研究成果
大規模データに対する主成分分析の性能を評価

2019年12月9日 BDRニュース
理研ニュース12月号に平谷伊智朗チームリーダー(発生エピジェネティクス研究チーム)らの研究が紹介されました

2019年9月17日 BDRニュース
1細胞RNA解析キットの商用化へ
2019年2月25日 研究成果
高速検索エンジン「CellFishing.jl」を開発