Team Director
Hiroki Shibuya
Ph.D.
Laboratory for Gametogenesis
LocationKobe / Developmental Biology Buildings
E-mailhiroki.shibuya[at]riken.jp
Please replace [at] with @.
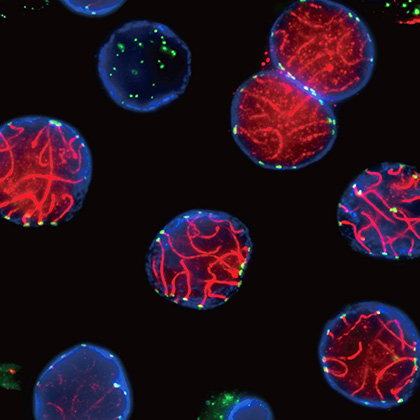
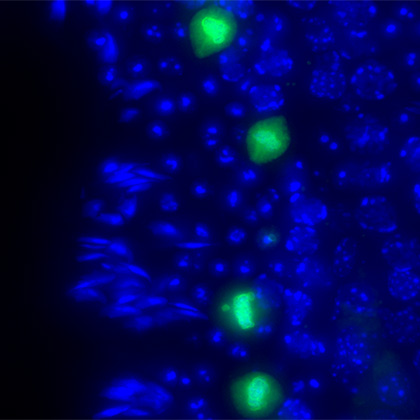
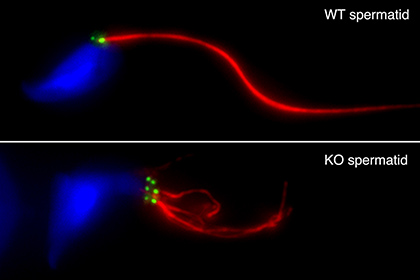
Even though organisms reach the end of their lives at the individual level, they can survive semi-permanently at the species level by refreshing the genetic and epigenetic information in their germ cells and passing it on to the next generation. In order to ensure these processes, germ cells undergo a unique cell division called meiosis, which halves the number of chromosomes, and then undergo differentiation into sperm and eggs (gametes). Our team combines mouse and nematode genetics, cytology, and biochemistry to study the molecular basis of gametogenesis. In particular, we focus on the role of spermatid centrosomes in prophase I chromosome movement, homologous recombination, chromosome segregation, and flagellum formation.
Selected Publications
Padmanaban S, Lambacher NJ, Tesmer VM, et al.
Caenorhabditis elegans telomere-binding proteins TEBP-1 and TEBP-2 adapt the Myb module to dimerize and bind telomeric DNA.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
121(16), e2316651121 (2024)
doi: 10.1073/pnas.2316651121
Zhang J, Ruiz M, Bergh PO, et al.
Regulation of meiotic telomere dynamics through membrane fluidity promoted by AdipoR2-ELOVL2.
Nature Communications
15(1), 2315 (2024)
doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46718-6
He S, Gillies JP, Zang JL, et al.
Distinct dynein complexes defined by DYNLRB1 and DYNLRB2 regulate mitotic and male meiotic spindle bipolarity.
Nature Communications
14(1), 1715 (2023)
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37370-7
Zhang K, Tarczykowska A, Gupta DK, et al.
The TERB1 MYB domain suppresses telomere erosion in meiotic prophase I.
Cell Reports
38(4), 110289 (2022)
doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.110289
Pendlebury DF, Zhang J, Agrawal R, et al.
Structure of a meiosis-specific complex central to BRCA2 localization at recombination sites.
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology
28(8), 671-680 (2021)
doi: 10.1038/s41594-021-00635-0
Yamamoto I, Zhang K, Zhang J, et al.
Telomeric double-strand DNA-binding proteins DTN-1 and DTN-2 ensure germline immortality in Caenorhabditis elegans.
eLife
10, e64104 (2021)
doi: 10.7554/eLife.64104
Zhang J, Gurusaran M, Fujiwara Y, et al.
The BRCA2-MEILB2-BRME1 complex governs meiotic recombination and impairs the mitotic BRCA2-RAD51 function in cancer cells.
Nature Communications
11(1), 2055 (2020)
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15954-x
Zhang J, Fujiwara Y, Yamamoto S, Shibuya H.
A meiosis-specific BRCA2 binding protein recruits recombinases to DNA double-strand breaks to ensure homologous recombination.
Nature Communications
10(1), 722 (2019)
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08676-2
Zhang J, Tu Z, Watanabe Y, Shibuya H.
Distinct TERB1 Domains Regulate Different Protein Interactions in Meiotic Telomere Movement.
Cell Reports
21(7), 1715-1726 (2017)
doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.10.061
Shibuya H, Hernández-Hernández A, Morimoto A, et al.
MAJIN Links Telomeric DNA to the Nuclear Membrane by Exchanging Telomere Cap.
Cell
163(5), 1252-1266 (2015)
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.10.030
Members
Hiroki Shibuya
Team Director
Morie Ishida
Research Scientist
Yutaka Takeda
Postdoctoral Researcher
Eriko Kajikawa
Technical Staff I